
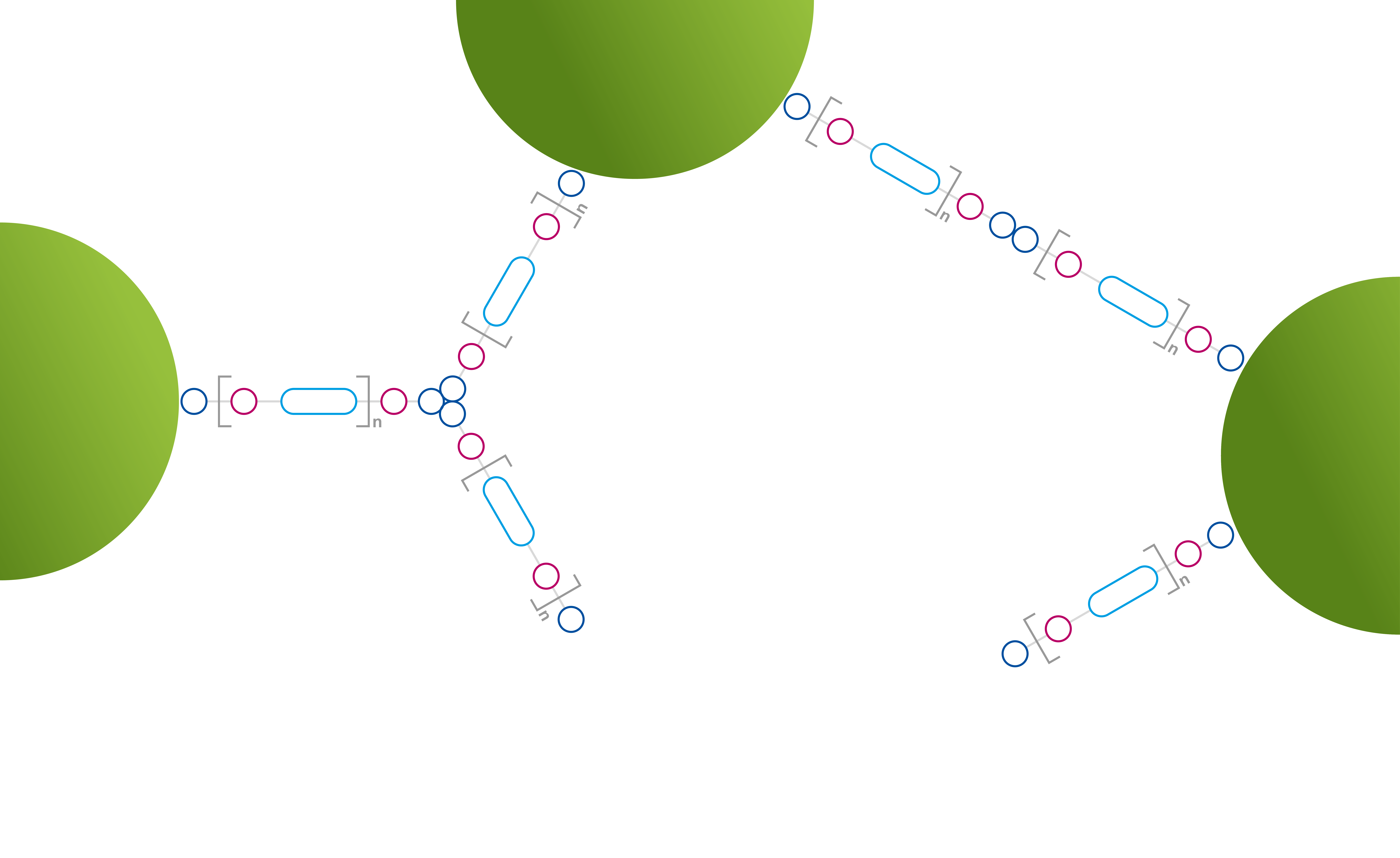
Polyurethane thickeners (PU thickeners) are widely used in the market and find use in a variety of different aqueous systems due to their liquid delivery form, easy handling, and wide range of applications. Due to their associative behavior and interaction with hydrophobic components of the formulation, it is necessary to have a wide variety of different products on the market to achieve the best possible effectiveness in terms of the desired rheological profile.
PU thickeners are characterized by the fact that they can be rheologically effective over the entire shear rate range. For this reason, a distinction is made between products for the low, medium and high shear ranges. With a suitable selection, storage stability, in-can viscosity, processability, and sag resistance can be adjusted. As a rule, various PU thickeners are combined with each other or used together with other rheology additives. Products for the low shear range primarily improve storage stability, behavior during transport, and sag resistance. They are also suitable for achieving high viscosities at very low dosage. For adjusting the in-can viscosity in the mid shear range, the most suitable products are those that do not increase the low-shear viscosity too much. These associative thickeners are also known as "KU drivers". Both low-shear and mid-shear thickeners produce a pseudoplastic flow behavior. Products that lead to a rather moderate viscosity increase with Newtonian flow behavior are particularly suitable for use in the high shear range. They improve the application properties, for example, by increasing the brush resistance when applied by brush or reducing the tendency to spatter when applied by roller.
The Newtonian flow behavior is also very well suited for spray application and ensures good substrate wetting and leveling. Thickeners for the high shear range are also called "ICI drivers".
Due to their associative behavior, PU thickeners always have a strong system-dependent effect. The strongest interaction is with the binder and depends not only on the binder type but also on the binder content: The higher the binder content, the stronger the effectiveness. Other formulation components can also influence the effectiveness of PU thickeners, as they affect the associative mechanism. These include, in particular, solvents, film-forming aids and surface-active substances.
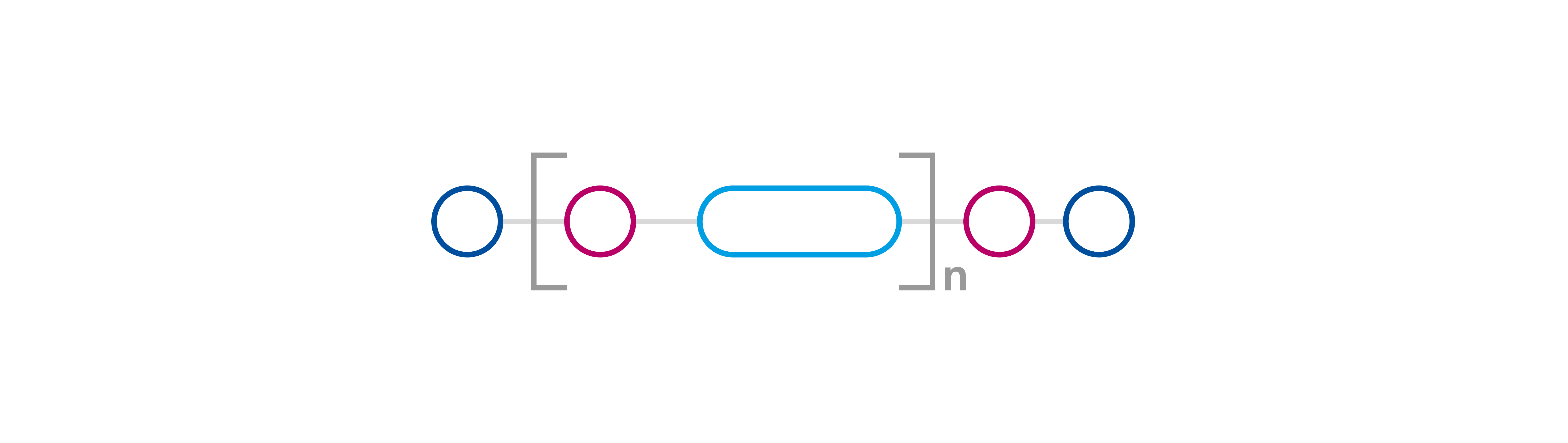
PU thickeners are higher molecular weight hydrophilic polymers that can have a linear, branched or star-shaped structure and contain hydrophobic groups. The hydrophobic groups are linked to the hydrophilic segments via urethane groups. For this reason, these products are also referred to as urethane thickeners or HEUR thickeners (HEUR = hydrophobically modified ethoxylated urethane). Since these thickeners do not contain any ionic groups, they are also known as non-ionic synthetic associative thickeners (NISAT). Depending on the desired area of effect, there are many ways of optimizing the application properties of PU thickeners. For example, it is possible to selectively adjust the chain length (molecular weight), the type and number of hydrophobic groups and the structure of the polymer in order to develop targeted products for the low, medium or high shear range. The presence of a hydrophobic formulation component, such as a binder dispersion, is essential in the effectiveness of polyurethane thickeners. Without it, they show no effectiveness in the system.
On this website we use cookies and similar functions to process end device information and personal data. The processing is used for purposes such as to integrate content, external services and elements from third parties, statistical analysis/measurement, personalized advertising and the integration of social media. Depending on the function, data is passed on to up to 9 third parties and processed by them. This consent is voluntary, not required for the use of our website and can be revoked at any time using the icon on the bottom left.